On the day of July 6th, 2016, a team comprising of members of Biome and ATREE went to Kaikondrahalli Lake in order to assess the quality of water. With the start of the monsoon season, the quantity of water that the lake receives increases, which also create situations of untreated sewage finding its way to the lake. Having that in mind, samples were picked up from key locations of the lake and were tested for physical and chemical parameters. Specifically, Nitrates (NO3) and Phosphates (PO4) were given for testing to a laboratory by the name of Nexus Test Labs.
Locations
4 locations were identified where samples were picked up for laboratory testing:
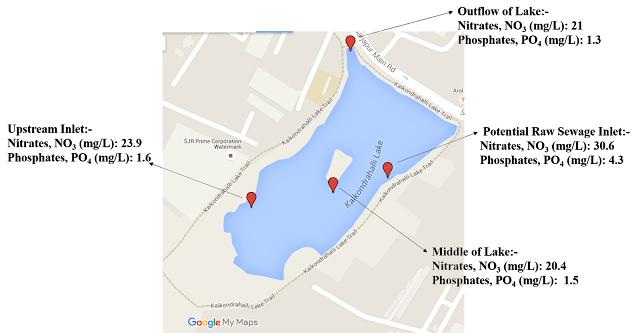
Upstream Inlet: A location near to the major inlet of the lake, on the Southern side. Water from the Kasavanahalli Lake and upstream dwellings that feed Kaikondrahalli Lake.
Middle of Lake: A sample was taken approximately at the middle of the lake, close to the island.
Potential Sewage Inlet: An inlet located on the Eastern side of the lake. There have been indication of raw untreated sewage entering the lake from this inlet. The source is potentially been identified as the lower income community residing right next to the lake.
Outflow: This sample was taken close to where the water exists the lake, on the North Western tip. The result would provide us with information of what quality of water flows further downstream towards Saul Kere.
Results
Nitrates and Phosphates
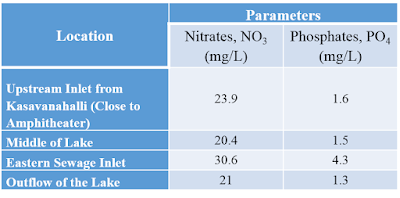
Here are the results that were provided from test conducted in the laboratory:-
The locations along with the results has also been displayed in the following figure:-
pH and Total Dissolved Solids
The pH and TDS values were also measured at varying locations within the lake, with an attempt to logically cover the stretch of the lake. Consistency was noticed with the pH values ranging between 8.3-8.9. TDS values also hovered between 430-460 mg/L.
Regulatory Standards
Standard IS: 10500- 2012 sanctioned by the Central Board of Pollution Control provide standards that need to be adhered to with respect to water being utilized for consumption. In the given standard, the maximum limit for Nitrates is identified as 45 mg/L. Currently it is unclear of a standard for Phosphates which not been provided by the relevant authorities.
Karnataka State Pollution Control Board (KSPCB) have standards of the quality of water that must be maintained in the output of sewage treatment plants, post treatment. The standard for Phosphates is given to be a maximum of 5 mg/L and no standard as of yet is adopted by KSPCB with respect to Nitrates.
However while comparing the results of the tests conducted for the lake samples with the given standards, it is clear with this data set that the water quality of the lake appears to be sufficiently acceptable. This conclusion however can be a lot more confirmed when multiple quality monitoring is conducted over time and with seasonal variations.

Its quite different from other posts. Thanks for sharing.
metering dosing pump manufacturer in india | chemical dosing system | water treatment equipments | chemical dosing system
Thanks for this article. I will also like to mention that it can always be hard when you find yourself in school and starting out to initiate a long credit score. There are many scholars who are merely trying to pull through and have a lengthy or beneficial credit history can be a difficult thing to have.